Azure Backup Disaster Recovery: 7 Ultimate Power Strategies
In today’s digital-first world, data is the lifeblood of every organization. When disaster strikes, having a robust Azure Backup Disaster Recovery plan isn’t just smart—it’s essential for survival and continuity.
Understanding Azure Backup Disaster Recovery: The Foundation

Azure Backup Disaster Recovery refers to a comprehensive strategy designed to protect data, applications, and IT infrastructure hosted on Microsoft Azure from unexpected outages, cyberattacks, or system failures. It combines automated backup solutions with orchestrated recovery processes to ensure business continuity.
What Is Azure Backup?
Azure Backup is a cloud-based service offered by Microsoft that enables organizations to back up their data across various environments—on-premises, hybrid, and cloud-native. It supports a wide range of workloads including virtual machines, SQL databases, file shares, and more.
- Backs up data to secure, scalable Azure storage
- Supports long-term retention policies
- Integrates seamlessly with Azure Monitor and Azure Security Center
By using Azure Backup, businesses eliminate the need for physical backup infrastructure, reducing costs and complexity. The service automatically encrypts data both in transit and at rest, ensuring compliance with global security standards like GDPR and HIPAA. Learn more about its capabilities at the official Microsoft Azure Backup documentation.
What Is Disaster Recovery in Azure?
Disaster Recovery (DR) in Azure goes beyond simple data backup. It involves replicating entire systems—such as virtual machines and applications—to a secondary region so they can be quickly restored in case of a major disruption.
- Leverages Azure Site Recovery (ASR) for workload replication
- Enables failover and failback between regions
- Supports RTO (Recovery Time Objective) and RPO (Recovery Point Objective) customization
Unlike traditional DR solutions that require dedicated hardware and complex configurations, Azure’s disaster recovery model is software-defined, scalable, and cost-efficient. This makes it ideal for organizations of all sizes aiming for high availability without massive capital investment.
“Disaster recovery is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity in an era where downtime can cost millions per hour.” — Microsoft Azure CTO
Why Azure Backup Disaster Recovery Is a Game-Changer
The integration of Azure Backup and Disaster Recovery transforms how organizations approach resilience. Instead of treating backup and recovery as separate functions, Azure unifies them into a single, intelligent ecosystem that responds dynamically to threats.
Cost Efficiency and Scalability
One of the most compelling advantages of Azure Backup Disaster Recovery is its pay-as-you-go pricing model. Organizations only pay for the storage and compute resources they use, avoiding upfront hardware costs.
- No need for secondary data centers
- Automatic scaling based on workload demands
- Granular control over retention policies to optimize spending
This flexibility allows startups and enterprises alike to implement enterprise-grade protection without over-provisioning. For example, a small business can start with basic VM backups and scale up to full geo-redundant disaster recovery as it grows.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
Data security is paramount, especially when dealing with sensitive information. Azure Backup Disaster Recovery incorporates multiple layers of protection to safeguard data integrity and confidentiality.
- End-to-end encryption using customer-managed or Microsoft-managed keys
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to limit who can initiate backups or restore operations
- Audit logging via Azure Monitor for compliance reporting
Additionally, Azure complies with over 90 global certifications, including ISO 27001, SOC 1/2, and FedRAMP. This makes it easier for regulated industries—like finance and healthcare—to meet strict data governance requirements while maintaining operational agility.
Core Components of Azure Backup Disaster Recovery
To fully leverage Azure Backup Disaster Recovery, it’s crucial to understand its key components and how they interact within the Microsoft cloud ecosystem.
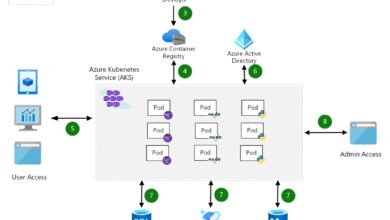
Azure Backup Vault (Recovery Services Vault)
The Recovery Services Vault is the central hub for managing backup and recovery operations in Azure. It acts as a secure container that stores backup data, policies, and metadata.
- Stores backup copies of VMs, databases, and on-premises servers
- Supports cross-region replication for added redundancy
- Allows policy-based automation for scheduling and retention
Each vault can be configured with specific access controls and monitoring settings, ensuring that only authorized personnel can manage critical recovery tasks. You can create multiple vaults to segment environments by department, region, or compliance level.
Azure Site Recovery (ASR)
Azure Site Recovery is the engine behind disaster recovery in Azure. It replicates virtual machines and physical servers from one location to another—either within Azure or from on-premises to Azure.
- Supports VMware, Hyper-V, and physical server replication
- Enables near-zero RPO with continuous data sync
- Facilitates non-disruptive disaster recovery drills
ASR integrates with Azure Automation and Logic Apps to enable custom workflows during failover events. This means organizations can automate not just the technical recovery but also notify stakeholders, update DNS records, or trigger incident response protocols.
“Azure Site Recovery reduced our RTO from 12 hours to under 15 minutes.” — IT Director, Global Financial Institution
Implementing Azure Backup Disaster Recovery: Step-by-Step
Deploying an effective Azure Backup Disaster Recovery strategy requires careful planning and execution. Below is a structured approach to get started.
Assess Your Workloads and Recovery Objectives
Before implementing any solution, identify which systems are critical and define your Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO).
- Classify workloads as Tier 1 (mission-critical), Tier 2 (important), or Tier 3 (non-critical)
- Determine acceptable downtime and data loss thresholds
- Map dependencies between applications and infrastructure
This assessment helps prioritize resources and allocate budget effectively. For instance, a Tier 1 application might require ASR with 5-minute RPO, while a Tier 3 system could rely on daily backups.
Configure Backup Policies and Schedules
Once workloads are classified, create tailored backup policies using the Azure portal or PowerShell.
- Set frequency (hourly, daily, weekly)
- Define retention periods (short-term and long-term)
- Enable geo-replication for critical data
Azure allows granular policy management through tags, making it easy to apply consistent rules across multiple resources. For example, tagging all production VMs with “Environment:Production” lets you apply a strict backup policy in one action.
Azure Backup Disaster Recovery for Hybrid Environments
Many organizations operate in hybrid environments, where some workloads run on-premises while others are in the cloud. Azure Backup Disaster Recovery excels in these scenarios by offering unified protection across both domains.
Protecting On-Premises Workloads
Azure Backup supports on-premises servers through the Microsoft Azure Recovery Services (MARS) agent. This lightweight software installs directly on Windows or Linux machines and enables seamless backup to the cloud.
- Backs up files, folders, and system state
- Supports application-consistent backups for SQL and Exchange
- Uses compression and deduplication to reduce bandwidth usage
For large enterprises with thousands of servers, Azure Backup Server (formerly DPM) provides centralized management and enhanced scalability. It acts as an intermediary backup server that aggregates data before sending it to Azure, minimizing network impact.
Replicating Hybrid VMs with Azure Site Recovery
For virtualized on-premises environments (VMware or Hyper-V), Azure Site Recovery enables seamless replication to Azure. This creates a cloud-based DR site that can be activated instantly during an outage.
- No changes required to existing VMs
- Supports multi-hypervisor environments
- Allows test failovers without affecting production
This capability is particularly valuable for organizations undergoing digital transformation. They can maintain legacy systems on-premises while building resilience in the cloud, preparing for a future fully cloud-native architecture.
Monitoring and Testing Your Azure Backup Disaster Recovery Plan
A plan is only as good as its ability to perform under pressure. Regular monitoring and testing are essential to ensure reliability.
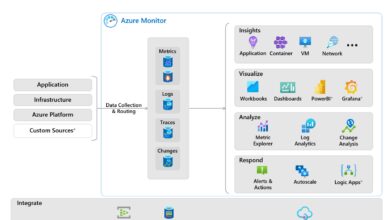
Using Azure Monitor and Alerts
Azure Monitor provides real-time visibility into backup and replication health. You can track job statuses, storage consumption, and replication lag.
- Create custom dashboards for DR metrics
- Set up alerts for failed backups or replication delays
- Integrate with ITSM tools like ServiceNow or Jira
For example, if a backup job fails three times in a row, an alert can be sent to the operations team via email, SMS, or webhook. This proactive approach prevents small issues from becoming catastrophic failures.
Conducting Disaster Recovery Drills
Testing your DR plan is not optional—it’s a best practice mandated by most compliance frameworks. Azure allows non-disruptive DR drills using isolated networks.
- Simulate regional outages without impacting live systems
- Validate application functionality post-failover
- Measure actual RTO and compare against targets
After each drill, generate a report to identify gaps and refine procedures. Over time, this iterative process builds confidence and improves organizational readiness.
“We run quarterly DR tests in Azure—each one gets faster and smoother.” — CIO, Healthcare Provider
Advanced Strategies for Azure Backup Disaster Recovery
For organizations seeking maximum resilience, advanced strategies can further enhance protection and automation.
Leveraging Immutable Backups to Fight Ransomware
With ransomware attacks on the rise, immutable backups are a powerful defense. Azure supports time-locked backups that cannot be deleted or altered during a specified period.
- Prevents attackers from encrypting or deleting backup data
- Complies with SEC and NIST guidelines for cyber resilience
- Configurable via Azure Blob Storage’s legal hold or retention policies
By enabling immutability, organizations ensure that even if production systems are compromised, clean backups remain available for recovery.
Automating Failover with Azure Automation and Runbooks
Manual failover processes are slow and error-prone. Azure Automation allows you to create runbooks—scripts that automate recovery workflows.
- Trigger failover based on health checks or external events
- Update DNS and load balancer configurations automatically
- Send notifications to stakeholders via Teams or Slack
For example, a runbook can detect a prolonged outage in the primary region, initiate ASR failover, redirect traffic, and post a status update—all without human intervention.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While Azure Backup Disaster Recovery offers immense benefits, organizations often face challenges during implementation.
Network Bandwidth Constraints
Initial replication of large datasets can consume significant bandwidth, potentially affecting production performance.
- Solution: Use offline seeding with Azure Import/Export service
- Solution: Schedule replication during off-peak hours
- Solution: Enable compression and WAN optimization features
By planning data transfer strategically, businesses can minimize network impact and accelerate deployment.
Complexity in Multi-Subscription or Multi-Tenant Setups
Enterprises with multiple Azure subscriptions or tenants may struggle with centralized management.
- Solution: Use Azure Lighthouse for cross-tenant management
- Solution: Implement Azure Policy to enforce backup compliance
- Solution: Centralize monitoring with Azure Monitor across subscriptions
These tools provide a unified control plane, reducing administrative overhead and ensuring consistency across environments.
What is the difference between Azure Backup and Azure Site Recovery?
Azure Backup focuses on creating point-in-time copies of data for recovery, while Azure Site Recovery is designed for workload replication and disaster recovery orchestration. Backup is ideal for file-level or database recovery, whereas Site Recovery enables full system failover to a secondary location.
Can I use Azure Backup Disaster Recovery for on-premises servers?
Yes, Azure Backup supports on-premises Windows and Linux servers via the MARS agent. Additionally, Azure Site Recovery can replicate VMware and Hyper-V virtual machines from on-premises data centers to Azure for disaster recovery purposes.
How does Azure ensure backup data security?
Azure encrypts backup data both in transit and at rest using AES-256 encryption. You can use Microsoft-managed keys or bring your own keys (BYOK) via Azure Key Vault for enhanced control. Access is restricted through RBAC and audit logs are maintained for compliance.
What are RTO and RPO in Azure Disaster Recovery?
RTO (Recovery Time Objective) is the maximum acceptable time to restore systems after a disruption. RPO (Recovery Point Objective) is the maximum acceptable amount of data loss measured in time. Azure allows you to configure both based on workload criticality.
How often should I test my disaster recovery plan?
It is recommended to test your Azure Backup Disaster Recovery plan at least quarterly. Regular testing ensures that recovery procedures work as expected and helps identify gaps before a real incident occurs.
Azure Backup Disaster Recovery is not just a technical solution—it’s a strategic imperative for modern businesses. By combining robust backup capabilities with intelligent disaster recovery orchestration, Azure empowers organizations to achieve resilience, compliance, and operational agility. Whether you’re protecting a single server or an entire hybrid estate, the tools and best practices outlined in this guide provide a solid foundation for safeguarding your digital future.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: