Azure Data Factory: 7 Powerful Features You Must Know
If you’re diving into cloud data integration, Azure Data Factory isn’t just another tool—it’s your ultimate powerhouse. Seamlessly connecting, transforming, and orchestrating data across clouds and on-premises, it’s revolutionizing how businesses handle data workflows with zero infrastructure hassles.
What Is Azure Data Factory and Why It Matters

Azure Data Factory (ADF) is Microsoft’s cloud-based data integration service that enables organizations to create data-driven workflows for orchestrating and automating data movement and transformation. Built on a serverless architecture, ADF allows developers, data engineers, and analysts to construct pipelines that extract, transform, and load (ETL) or extract, load, and transform (ELT) data from diverse sources.
Core Definition and Purpose
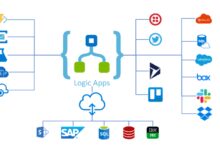
Azure Data Factory serves as a central hub for data integration in the Microsoft Azure ecosystem. It allows users to create, schedule, and manage data pipelines that automate the flow of data from various sources—such as databases, SaaS applications, and big data systems—into destinations like Azure Data Lake, Azure Synapse Analytics, or Power BI.
- Enables hybrid data integration across cloud and on-premises environments.
- Supports both code-free visual tools and code-based development using JSON, .NET, or Python.
- Integrates natively with other Azure services like Azure Databricks, Azure SQL Database, and Azure Blob Storage.
According to Microsoft’s official documentation, Azure Data Factory simplifies complex data workflows by abstracting infrastructure management, allowing teams to focus on data logic rather than server provisioning.
Evolution from SSIS to Cloud-Native ETL
Before ADF, many enterprises relied on SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) for ETL processes. While powerful, SSIS required on-premises infrastructure, manual scaling, and complex deployment models. Azure Data Factory emerged as its cloud-native successor, offering elasticity, global scalability, and seamless integration with modern data platforms.
- ADF eliminates the need for physical servers, reducing operational overhead.
- It supports modern data formats like Parquet, ORC, and Avro out of the box.
- ADF pipelines can be version-controlled using Git, enabling DevOps practices in data engineering.
“Azure Data Factory bridges the gap between traditional ETL and modern data orchestration, making it indispensable in today’s hybrid data landscape.” — Microsoft Azure Architecture Center
Key Components of Azure Data Factory
To fully leverage Azure Data Factory, it’s essential to understand its core components. Each element plays a critical role in building robust, scalable data pipelines that meet enterprise requirements.
Data Pipelines and Activities
A pipeline in Azure Data Factory is a logical grouping of activities that perform a specific task. Activities are the building blocks of a pipeline and define the actions to be performed on your data.
- Data Movement Activities: Copy data between sources and sinks (e.g., from SQL Server to Azure Blob Storage).
- Data Transformation Activities: Execute transformations using services like Azure Databricks, HDInsight, or Azure Functions.
- Control Activities: Manage workflow logic with constructs like If Condition, ForEach, and Execute Pipeline.
For example, a pipeline might start with a Copy Activity to ingest sales data from Salesforce, followed by a Databricks Notebook Activity to clean and enrich the data, and conclude with a Stored Procedure Activity to load results into a data warehouse.
Linked Services and Datasets
Linked Services define the connection information needed to connect to external resources. Think of them as connection strings with metadata about the data store or compute service.
- They support authentication via keys, service principals, managed identities, or OAuth.
- Examples include Azure SQL Database, Amazon S3, Oracle, and REST APIs.
- Security is enhanced through Azure Key Vault integration for credential storage.
Datasets, on the other hand, represent the structure and location of data within a data store. They are used as inputs and outputs in pipeline activities.
- A dataset can point to a specific table, file, or container.
- They support schema validation and data type mapping.
- Parameterization allows dynamic dataset definitions at runtime.
For instance, a dataset might reference a CSV file in an Azure Blob Storage container, specifying the folder path and file name pattern.
Integration Runtime (IR)
The Integration Runtime is the compute infrastructure that Azure Data Factory uses to provide data integration capabilities across different network environments.
- Azure IR: Used for public cloud data movement and transformation.
- Self-Hosted IR: Enables data transfer between cloud and on-premises systems securely.
- Managed Virtual Network IR: Provides secure, isolated execution for sensitive workloads.
The Self-Hosted IR is particularly crucial for organizations with legacy systems behind firewalls. It acts as a bridge, allowing ADF to securely access databases like on-prem SQL Server or SAP without exposing them to the internet.
How Azure Data Factory Enables Data Orchestration
One of the most powerful aspects of Azure Data Factory is its ability to orchestrate complex workflows across multiple systems and services. Unlike simple ETL tools, ADF provides granular control over execution order, dependencies, and error handling.
Workflow Automation with Pipelines
Pipelines in Azure Data Factory are not just linear sequences—they are intelligent workflows capable of conditional branching, looping, and parallel execution.
- Use the Execute Pipeline activity to call child pipelines, enabling modular design.
- Leverage Wait and Until activities for polling-based workflows.
- Implement Web Activity to trigger external APIs or microservices.
This orchestration capability is vital for scenarios like end-of-day financial reporting, where multiple data sources must be processed in a specific sequence before generating dashboards.
Scheduling and Triggering Mechanisms
ADF supports multiple ways to trigger pipeline execution, ensuring flexibility for different business needs.
- Schedule Triggers: Run pipelines on a fixed schedule (e.g., daily at 2 AM).
- Event-Based Triggers: Start pipelines when a file is uploaded to Blob Storage or a message arrives in Event Hubs.
- Tumbling Window Triggers: Ideal for time-series data processing with dependency chaining.
For example, an e-commerce company might use an event-based trigger to process new order files as soon as they land in Azure Data Lake, ensuring real-time analytics readiness.
Microsoft provides detailed guidance on pipeline execution and triggers in ADF, emphasizing their role in building responsive data architectures.
Data Transformation Capabilities in Azure Data Factory
While data movement is important, true value comes from transformation. Azure Data Factory doesn’t just move data—it empowers teams to enrich, cleanse, and analyze it using a variety of integrated services.
Mapping Data Flows: No-Code Transformation
Mapping Data Flows is ADF’s visual, code-free environment for building data transformations. It uses a drag-and-drop interface powered by Apache Spark, running on a serverless compute layer.
- Supports over 100 transformation types, including filter, aggregate, join, pivot, and derived column.
- Enables schema drift handling—automatically adapting to changes in input data structure.
- Provides data preview and debugging tools for faster development.
Data engineers can build complex transformations without writing a single line of code, significantly reducing development time and increasing accessibility for non-developers.
Integration with Azure Databricks and HDInsight
For advanced analytics and machine learning workflows, Azure Data Factory integrates seamlessly with Azure Databricks and HDInsight.
- Use Databricks Notebook Activity to run Python, Scala, or SQL notebooks.
- Leverage HDInsight Hive Activity for large-scale batch processing on Hadoop clusters.
- Pass parameters from ADF to notebooks for dynamic execution.
This integration allows data science teams to operationalize ML models by embedding them into production data pipelines. For instance, a fraud detection model trained in Databricks can be triggered daily by ADF to score new transactions.
Custom Logic with Azure Functions and Logic Apps
Sometimes, off-the-shelf transformations aren’t enough. Azure Data Factory allows integration with Azure Functions and Logic Apps to inject custom business logic.
- Use Azure Function Activity to execute small, stateless functions (e.g., sending notifications or validating data).
- Integrate Logic Apps for enterprise application integration (EAI) scenarios like syncing CRM systems.
- Supports REST, HTTP, and webhook-based communication.
This extensibility makes ADF not just a data tool, but a full-fledged integration platform.
Security and Compliance in Azure Data Factory
In enterprise environments, security isn’t optional—it’s mandatory. Azure Data Factory provides robust mechanisms to ensure data privacy, access control, and regulatory compliance.
Authentication and Access Control
ADF integrates with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) for identity management and role-based access control (RBAC).
- Assign roles like Data Factory Contributor, Reader, or Operator to users and groups.
- Use Managed Identities to authenticate with other Azure services without storing credentials.
- Supports multi-factor authentication (MFA) and conditional access policies.
For example, a data engineer might have Contributor access to create pipelines, while an analyst has Reader access to monitor runs without modifying resources.
Data Encryption and Network Security
All data in transit and at rest is encrypted by default in Azure Data Factory.
- Uses TLS 1.2+ for data in motion.
- Leverages Azure Storage Service Encryption (SSE) for data at rest.
- Supports Private Endpoints to block public internet access to ADF resources.
When combined with VNet injection and firewall rules, these features help organizations meet strict compliance standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2.
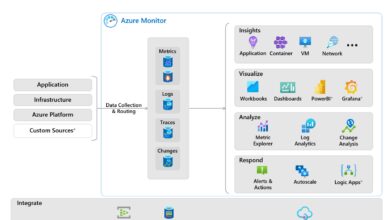
Audit Logging and Monitoring
Comprehensive logging is available through Azure Monitor and Log Analytics.
- Track pipeline runs, activity durations, and failure reasons.
- Set up alerts for failed executions or long-running jobs.
- Export logs to Sentinel for advanced threat detection.
These capabilities are essential for maintaining operational transparency and meeting audit requirements.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting Azure Data Factory Pipelines
Even the best-designed pipelines can fail. Azure Data Factory provides powerful tools to monitor, debug, and optimize pipeline performance.
Monitoring via Azure Monitor and Metrics
The Monitoring hub in ADF gives real-time visibility into pipeline execution.
- View run history, durations, and statuses (Success, Failed, In Progress).
- Analyze metrics like CPU usage, data read/write rates, and queue lengths.
- Create custom dashboards using Azure Portal widgets.
You can also integrate with Application Insights for deeper telemetry and correlation with other services.
Debugging Failed Pipeline Runs
When a pipeline fails, ADF provides detailed error messages and logs to aid troubleshooting.
- Check the Activity Output tab for specific error codes (e.g., 404 Not Found, timeout).
- Use the Run ID to trace execution across distributed components.
- Leverage Self-Hosted IR Logs for connectivity issues with on-prem systems.
Common issues include incorrect connection strings, firewall blocks, schema mismatches, or resource throttling—each identifiable through ADF’s diagnostic tools.
Optimizing Performance and Cost
Efficiency matters. Poorly designed pipelines can lead to high costs and slow performance.
- Use Copy Activity Performance Tuning options like parallel copies and batch sizes.
- Scale Integration Runtime nodes based on workload demand.
- Monitor data flow debug cluster usage to avoid unnecessary compute spend.
Microsoft recommends using the Copy Activity performance guide to optimize throughput and reduce latency.
Real-World Use Cases of Azure Data Factory
Theoretical knowledge is valuable, but real-world applications show Azure Data Factory’s true power. Let’s explore how industries are leveraging ADF to solve complex data challenges.
Healthcare: Integrating Patient Data Across Systems
Hospitals often have data trapped in siloed systems—EMRs, lab systems, billing platforms. ADF helps unify this data securely.
- Extract patient records from on-prem EHR systems using Self-Hosted IR.
- Transform and anonymize sensitive data using Mapping Data Flows.
- Load into Azure Synapse for analytics and reporting.
This enables faster diagnosis, better care coordination, and compliance with HIPAA regulations.
Retail: Real-Time Inventory and Sales Analytics
Retailers need up-to-the-minute insights to manage stock and promotions.
- Ingest point-of-sale (POS) data from stores via event triggers.
- Combine with online sales from e-commerce platforms.
- Run daily ELT pipelines to update dashboards in Power BI.
With ADF, a national retailer can process millions of transactions nightly and generate same-day reports for store managers.
Finance: Automating Regulatory Reporting
Banks must generate reports for regulators like the SEC or Basel Committee.
- Orchestrate multi-step pipelines that pull data from core banking systems.
- Apply business rules and validations using Databricks.
- Generate PDF/Excel reports and email them via Logic Apps.
ADF ensures consistency, auditability, and timely delivery of critical financial reports.
Best Practices for Using Azure Data Factory
To get the most out of Azure Data Factory, follow these proven best practices that top data teams use in production environments.
Design Modular and Reusable Pipelines
Avoid monolithic pipelines. Break them into smaller, reusable components.
- Create template pipelines for common tasks (e.g., data ingestion, error logging).
- Use parameters and variables to make pipelines dynamic.
- Leverage the Execute Pipeline activity to chain workflows.
This improves maintainability and reduces duplication.
Implement CI/CD with Azure DevOps
Treat your data pipelines like code. Use Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) to manage changes safely.
- Store ADF JSON definitions in Git repositories.
- Use Azure DevOps or GitHub Actions to deploy pipelines across dev, test, and prod environments.
- Validate changes with automated tests before promotion.
Microsoft provides a comprehensive CI/CD guide for ADF, including ARM template usage and branching strategies.
Plan for Error Handling and Retry Logic
Failures happen. Design pipelines to handle them gracefully.
- Set retry policies for transient errors (e.g., network timeouts).
- Use Try-Catch patterns with Execute Pipeline and If Condition activities.
- Log errors to Azure Monitor or a dedicated error queue.
Proactive error handling prevents data loss and ensures pipeline resilience.
What is Azure Data Factory used for?
Azure Data Factory is used to create data integration workflows that automate the movement and transformation of data across cloud and on-premises sources. It’s commonly used for ETL/ELT processes, data warehousing, real-time analytics, and orchestrating data science pipelines.
Is Azure Data Factory a ETL tool?
Yes, Azure Data Factory is a cloud-based ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT tool. It supports both patterns by allowing data transformation within the pipeline using Mapping Data Flows or external services like Azure Databricks and Synapse Analytics.
How much does Azure Data Factory cost?
Azure Data Factory pricing is based on usage: activity runs, data movement, and data flow debug hours. The service offers a free tier with limited monthly activity runs, and pay-as-you-go pricing thereafter. Costs vary based on region, volume, and complexity of operations.
Can Azure Data Factory replace SSIS?
Yes, Azure Data Factory can replace SSIS for most use cases, especially in cloud or hybrid environments. It offers enhanced scalability, native cloud integration, and modern DevOps support, making it the preferred choice for organizations migrating from on-premises ETL solutions.
How do I get started with Azure Data Factory?
To get started, create a Data Factory resource in the Azure portal, use the visual interface (Data Factory Studio) to build your first pipeline, and connect to data sources using linked services. Microsoft offers free learning paths and sandbox environments to practice without cost.
Azure Data Factory is more than just a data integration tool—it’s a comprehensive orchestration engine that empowers organizations to build scalable, secure, and intelligent data workflows. From automating ETL processes to enabling real-time analytics and supporting advanced data science pipelines, ADF stands at the heart of modern data architectures. By leveraging its powerful features like visual data flows, hybrid connectivity, and enterprise-grade security, businesses can unlock the full potential of their data. Whether you’re replacing legacy SSIS packages or building cloud-native data platforms, Azure Data Factory provides the flexibility, performance, and reliability needed to succeed in today’s data-driven world.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: