Azure SQL Database: 7 Powerful Features You Must Know
Looking for a reliable, scalable, and secure cloud database? Azure SQL Database delivers unmatched performance with intelligent automation and enterprise-grade security—perfect for modern applications.
What Is Azure SQL Database?

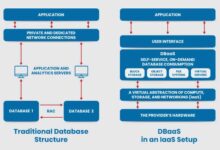
Azure SQL Database is Microsoft’s fully managed relational database service built on the Microsoft SQL Server engine, hosted in the cloud. As a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) offering, it eliminates the need for organizations to manage physical infrastructure, middleware, or even most database administration tasks. This allows developers and IT teams to focus on building applications rather than maintaining servers.
Core Architecture and Cloud Integration
At its foundation, Azure SQL Database runs on a scalable, high-availability infrastructure powered by Microsoft Azure data centers. It leverages the same SQL Server database engine as on-premises deployments but is optimized for cloud workloads. This means you get familiar T-SQL language support, stored procedures, views, and security models—without the overhead of hardware provisioning.
- Runs on Microsoft Azure’s global network of data centers
- Automatically replicates data across multiple nodes for redundancy
- Supports seamless integration with Azure Active Directory, Azure Monitor, and Azure DevOps
Because it’s a PaaS solution, Azure handles patching, backups, upgrades, and health monitoring. You simply connect your applications using standard tools like SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), Visual Studio, or any ODBC/JDBC-compatible client.
Differences Between Azure SQL Database and SQL Server
While both share the same core engine, there are key architectural and operational differences. Unlike traditional SQL Server, Azure SQL Database does not allow direct access to the underlying operating system or file system. This enhances security and simplifies management but limits certain advanced configurations.
- No
salogin orsysadminrole access - Some system databases (e.g.,
tempdb) are managed automatically - Extended stored procedures and CLR integrations have restrictions
Additionally, Azure SQL Database supports two deployment models: single databases and elastic pools. This flexibility allows businesses to scale resources based on workload demands without over-provisioning.
“Azure SQL Database enables organizations to shift from database management to database innovation.” — Microsoft Azure Documentation
Key Benefits of Using Azure SQL Database
Organizations worldwide are migrating to Azure SQL Database because it offers a compelling mix of performance, scalability, and cost-efficiency. Whether you’re running a small web app or a large enterprise system, this cloud-native database adapts to your needs.
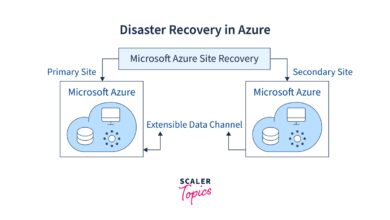
Automatic High Availability and Disaster Recovery
One of the standout features of Azure SQL Database is its built-in high availability. Every database is automatically protected with a 99.99% availability SLA. Behind the scenes, Microsoft replicates your data synchronously across three replicas within an Azure region using Always On Availability Groups.
- Automatic failover in case of hardware or software failure
- Geo-replication options for cross-region redundancy
- Point-in-time restore capabilities up to 35 days (depending on service tier)
For mission-critical applications, you can enable active geo-replication, which allows up to four readable secondary databases in different Azure regions. This not only improves disaster recovery readiness but also enables read-scale workloads for global applications.
Intelligent Performance Optimization
Azure SQL Database uses AI-driven insights to continuously monitor and optimize query performance. The service includes Automatic Tuning, which can identify inefficient queries and suggest or apply index changes without human intervention.
- Automatic index creation and removal
- Parameter sensitivity analysis to prevent plan regression
- Real-time performance monitoring via Query Performance Insight
Developers benefit from reduced latency and faster response times, while DBAs save hours of manual tuning. According to Microsoft, customers have seen up to a 30% improvement in workload performance after enabling automatic tuning.
Deployment Models: Single Database vs. Elastic Pool
Azure SQL Database offers two primary deployment models: single databases and elastic pools. Choosing the right one depends on your application architecture, workload patterns, and budget.
Single Database: Ideal for Isolated Workloads
The single database model is perfect for applications that require dedicated resources and predictable performance. Each database operates independently with its own compute, memory, and I/O allocation.
- Suitable for production apps with stable usage patterns
- Easy to manage and monitor individually
- Can be scaled up or down in seconds via the Azure portal or API
You can choose from various service tiers—Basic, Standard, Premium, and Business Critical—each offering different levels of performance, storage, and features like in-memory OLTP and advanced threat protection.
Elastic Pools: Cost-Efficient Scaling for Multiple Databases
When managing multiple databases (e.g., SaaS applications with per-tenant databases), elastic pools offer a more economical solution. Instead of assigning fixed resources to each database, you allocate a shared pool of compute (eDTUs or vCores) that all databases in the pool can draw from.
- Reduces costs by pooling resources across low-usage databases
- Handles unpredictable spikes in individual databases without over-provisioning
- Supports up to 100 databases per pool (depending on configuration)
Elastic pools are especially useful for development environments, multi-tenant applications, or microservices architectures where database usage varies significantly across instances.
Security and Compliance in Azure SQL Database
Security is a top priority for any cloud database, and Azure SQL Database provides a comprehensive suite of tools to protect your data at rest, in transit, and during access.
Data Encryption and Threat Detection
All data in Azure SQL Database is encrypted by default using Transparent Data Encryption (TDE). This ensures that your database files and backups are protected from unauthorized access, even if physical media is compromised.
- TDE uses AES-256 encryption and integrates with Azure Key Vault for customer-managed keys
- Dynamic Data Masking hides sensitive data from non-privileged users
- Always Encrypted allows clients to encrypt sensitive columns end-to-end
In addition, Advanced Data Protection includes features like Threat Detection, which monitors for suspicious activities such as SQL injection attempts or anomalous login patterns. Alerts are sent directly to administrators via email or integrated with Azure Security Center.
Authentication and Access Control
Azure SQL Database supports two authentication modes: SQL authentication and Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) authentication. While SQL authentication uses username/password pairs, Azure AD provides centralized identity management with multi-factor authentication (MFA) and conditional access policies.
- Enforce role-based access control (RBAC) at the server and database level
- Integrate with enterprise identity providers via federation
- Use contained database users for easier migration and management
By combining Azure AD with firewall rules and private link connectivity, organizations can create a zero-trust security model that minimizes exposure to external threats.
Scalability and Performance Tiers
One of the biggest advantages of Azure SQL Database is its ability to scale resources on demand. Whether you need more CPU, memory, or I/O, you can adjust your service tier in minutes—without downtime.
Provisioned Compute: DTUs and vCores
Azure SQL Database offers two purchasing models: the DTU-based model and the vCore-based model. The DTU (Database Transaction Unit) model bundles compute, memory, and I/O into predefined tiers (Basic, S0–S12, P1–P15). It’s simple to understand but less flexible.
- DTUs are ideal for predictable, steady-state workloads
- Limited visibility into underlying hardware specifications
- Harder to compare with on-premises SQL Server performance
The vCore model, on the other hand, gives you granular control over compute, storage, and licensing. You can choose the number of vCores, memory size, and even the hardware generation (e.g., Gen5, DC-series).
- Greater transparency and flexibility
- Support for hybrid benefit (use existing SQL Server licenses)
- Better alignment with on-premises performance expectations
Both models support auto-scaling through Azure Automation or Logic Apps, allowing you to respond dynamically to traffic spikes.
Serverless Option: Pay-Per-Session Pricing
For intermittent or unpredictable workloads, Azure SQL Database offers a serverless compute tier. This option automatically pauses the database during inactivity and resumes when a query arrives, charging only for the time the database is active.
- Ideal for dev/test environments, low-traffic apps, or event-driven systems
- Cost savings of up to 90% compared to always-on databases
- Configurable auto-pause delay (30 minutes to 7 days)
While serverless introduces a slight cold-start delay, it’s a game-changer for cost-conscious teams looking to optimize cloud spending.
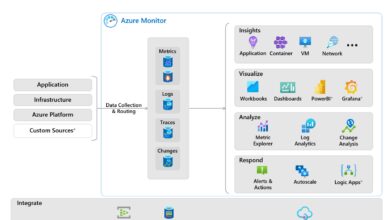
Monitoring, Management, and Automation
Effective database management requires real-time insights, proactive alerts, and automated workflows. Azure SQL Database integrates seamlessly with Azure Monitor, Log Analytics, and Automation services to provide full observability.
Query Performance Insight and Metrics
Query Performance Insight (QPI) is a built-in tool that helps you identify the most resource-intensive queries. It visualizes CPU, duration, and execution count over time, making it easy to pinpoint bottlenecks.
- Analyze top queries by CPU, I/O, or duration
- Compare performance across time periods
- Drill down into query text and execution plans
Additionally, Azure Monitor collects metrics like DTU percentage, storage usage, and deadlocks. These can be visualized in dashboards or used to trigger alerts when thresholds are exceeded.
Automated Backups and Restore Options
Every Azure SQL Database comes with automated backups enabled by default. Full backups are taken weekly, differential backups daily, and transaction log backups every 5–10 minutes.
- Point-in-time restore (PITR) available for up to 35 days
- Long-term retention (LTR) policies for compliance (up to 10 years)
- Geo-restore from replicated backups in secondary regions
You can also export databases to BACPAC files for archival or migrate them to other platforms. The entire process can be automated using PowerShell, Azure CLI, or REST APIs.
Migration Strategies to Azure SQL Database
Migrating from on-premises SQL Server or other cloud databases to Azure SQL Database requires careful planning. Microsoft provides several tools and methodologies to ensure a smooth transition.
Using Azure Database Migration Service (DMS)
Azure Database Migration Service (DMS) is a fully managed service that supports online (zero-downtime) migrations from SQL Server to Azure SQL Database. It assesses your source database for compatibility issues and performs continuous data synchronization until cutover.
- Supports heterogeneous migrations (e.g., Oracle to SQL)
- Integrates with Azure Migrate for discovery and assessment
- Minimizes application downtime during migration
For large-scale migrations, DMS can be combined with replication technologies like Transactional Replication or Change Data Capture (CDC).
Data Migration Assistant (DMA) for Assessment
Before migration, it’s crucial to evaluate your database for potential issues. The Data Migration Assistant (DMA) scans your SQL Server instance and generates a detailed report on compatibility, performance, and security recommendations.
- Identifies deprecated features and unsupported syntax
- Suggests index and schema optimizations
- Recommends security best practices
DMA also supports post-migration validation to ensure data integrity and performance parity.
Integration with Modern Application Architectures
Azure SQL Database is designed to work seamlessly with modern development frameworks, microservices, and serverless computing platforms.
Support for APIs and Development Tools
Developers can interact with Azure SQL Database using a wide range of languages and frameworks, including .NET, Java, Node.js, Python, and PHP. The database supports RESTful APIs through Azure API Management and integration with Azure Functions.
- Use Entity Framework, Dapper, or raw ADO.NET for data access
- Leverage Azure Logic Apps for workflow automation
- Connect via REST using Azure SQL REST API (preview)
Visual Studio and Azure Data Studio provide rich development experiences with IntelliSense, debugging, and schema comparison tools.
Microservices and Containerized Deployments
In microservices architectures, each service often requires its own database. Azure SQL Database supports this pattern through lightweight, independently scalable databases. When combined with Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), you can deploy containerized apps that connect securely to SQL Database using private endpoints.
- Isolate tenant data in multi-tenant SaaS apps
- Use connection pooling and retry logic for resilience
- Implement circuit breakers and health checks in application code
This modular approach improves fault isolation and enables independent scaling of services.
What is Azure SQL Database?
Azure SQL Database is a fully managed Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) relational database powered by Microsoft SQL Server. It runs in the cloud, offering high availability, automatic backups, intelligent performance tuning, and robust security features without requiring infrastructure management.
How much does Azure SQL Database cost?
Pricing depends on the service tier (DTU or vCore), compute size, storage, and features like backup retention. Costs range from a few dollars per month for basic tiers to thousands for high-performance Business Critical instances. The serverless option offers pay-per-use pricing, ideal for intermittent workloads.
Can I migrate my on-premises SQL Server to Azure SQL Database?
Yes, you can migrate using tools like Azure Database Migration Service (DMS) and Data Migration Assistant (DMA). These tools assess compatibility, transfer schema and data, and support online migrations with minimal downtime.
Does Azure SQL Database support stored procedures and triggers?
Yes, Azure SQL Database supports most T-SQL features, including stored procedures, functions, views, and triggers. However, some extended stored procedures and CLR integrations are restricted due to the managed nature of the service.
How do I secure my Azure SQL Database?
Use Azure Active Directory authentication, configure firewall rules, enable Transparent Data Encryption (TDE), set up Advanced Threat Protection, and apply role-based access control (RBAC). For maximum security, use Private Link to block public internet access.
Azure SQL Database is more than just a cloud version of SQL Server—it’s a powerful, intelligent, and secure database platform designed for the modern era. With automatic scaling, built-in AI optimization, enterprise-grade security, and seamless integration into the Azure ecosystem, it empowers organizations to build scalable, resilient, and high-performance applications. Whether you’re a startup or a global enterprise, Azure SQL Database provides the tools you need to succeed in the cloud.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: